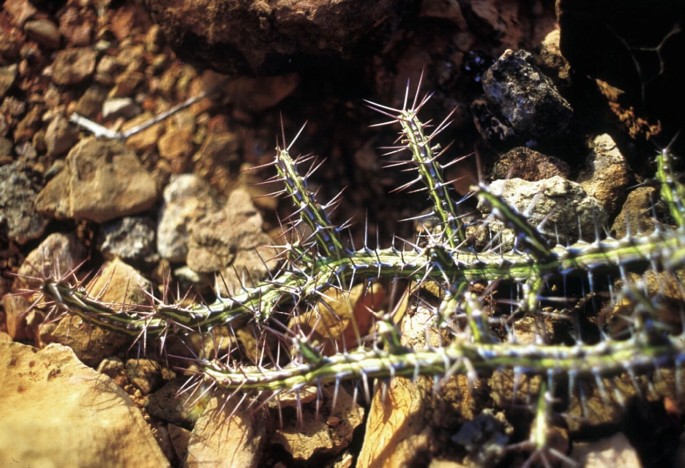
The Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, spans across North Africa, covering approximately 9.2 million square kilometers.
Known for its harsh and extreme conditions, the Sahara experiences scorching temperatures during the day, plummeting to near-freezing at night, with minimal and sporadic rainfall.
These conditions create a challenging environment for any form of life, particularly plants. That is why only resilient plants have succeeded in overcoming harsh conditions.
Table of Contents
Toggle7. Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera)
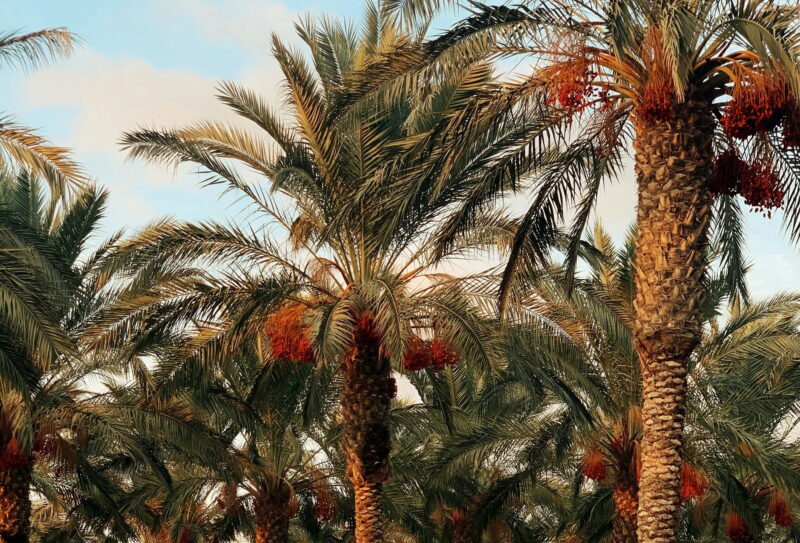

- Key Characteristics:
- Deep root systems that can reach groundwater
- Ability to store water in trunk and leaves
- Tall, slender trunk with large, feathery leaves
- Produces nutritious and long-lasting fruit
The date palm is one of the most iconic plants of the Sahara Desert. The plant has been cultivated for thousands of years, providing a vital source of food, shelter, and materials for desert-dwelling communities. The date palm’s fruit, dates, are highly nutritious and can be stored for long periods, making them an essential part of the diet in arid regions.
Date palms have a deep cultural and historical significance in many desert societies. They are often seen as symbols of life and prosperity in an otherwise desolate landscape. Their presence is a testament to the ingenuity of human cultivation practices in harmony with natural adaptations.
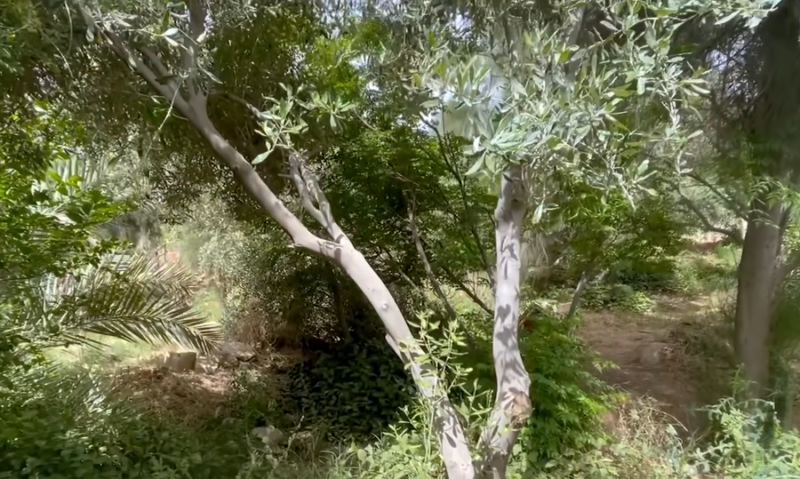
6. Laperinne’s Olive Tree (Olea europaea subsp. laperrinei)

- Key Characteristics:
- Vegetative reproduction capabilities
- Drought-resistant features
- Grows at higher elevations in the central Sahara
- Provides ecological benefits like soil stabilization
Laperinne’s olive tree, a subspecies of the more commonly known olive tree, is native to the mountainous regions of the central Sahara. Unlike its Mediterranean relatives, Laperinne’s olive tree has adapted to the arid and harsh conditions of the desert. Ecologically, Laperinne’s olive tree plays a vital role in its habitat. It provides shade and shelter for various desert animals and helps stabilize the soil, preventing erosion. The tree’s ability to reproduce vegetatively ensures its survival even in the most challenging conditions, where seed germination might be less reliable.
5. Tamarisk (Tamarix spp.)

- Key Characteristics:
- Salt tolerance
- Deep root systems
- Slender branches and small, scale-like leaves
- Role in combating desertification
They are well-known for their ability to thrive in saline environments, a characteristic that sets them apart from many other plants. Tamarisks can grow up to 15 meters tall, with slender branches and small, scale-like leaves that minimize water loss. These plants have a significant ecological impact in the Sahara. They are often used for land reclamation and to combat desertification due to their ability to stabilize soil and reduce wind erosion. Tamarisks also provide habitat and food for various desert species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the region.
The tree is also found in the Bible, in Genesis 21:33:
“Abraham planted a tamarisk tree in Beer Sheba. There he worshiped the Lord, the eternal God.”
4. Acacia Tree (Acacia spp.)

- Key Characteristics:
- Long tap roots that access deep water sources
- Small, pinnate leaves to minimize water loss
- Thorny branches for protection
- Provides resources for both wildlife and humans
They are characterized by their thorny branches and small, pinnate leaves, which reduce water loss. Acacias can vary greatly in size, from small shrubs to large trees, and are often found in wadis and other areas where water is more accessible. These trees are crucial for both local wildlife and human populations.
They provide food and habitat for numerous desert animals, including:
- Insects
- Birds
- Mammals
For humans, acacia trees offer valuable resources such as wood for fuel and building materials, as well as gum arabic, which is used in food and industrial products.
3. Sahara Lovegrass (Eragrostis tremula)
- Key Characteristics:
- Extensive root system for moisture access
- Ability to grow in sandy soils
- Helps prevent desertification by stabilizing soil
- Provides habitat and food for desert wildlife
Sahara lovegrass is a resilient grass species that plays a critical role in preventing desertification. It typically grows in sandy soils and can form dense tufts that help stabilize the sand. The grass is well adapted to the arid conditions of the Sahara, with an extensive root system that allows it to access moisture deep underground. The primary ecological role of Sahara lovegrass is soil stabilization, which helps prevent the spread of desert conditions. It reduces erosion and provides a habitat for other plant species to establish themselves. It serves as a food source for herbivores, contributing to the desert food web.
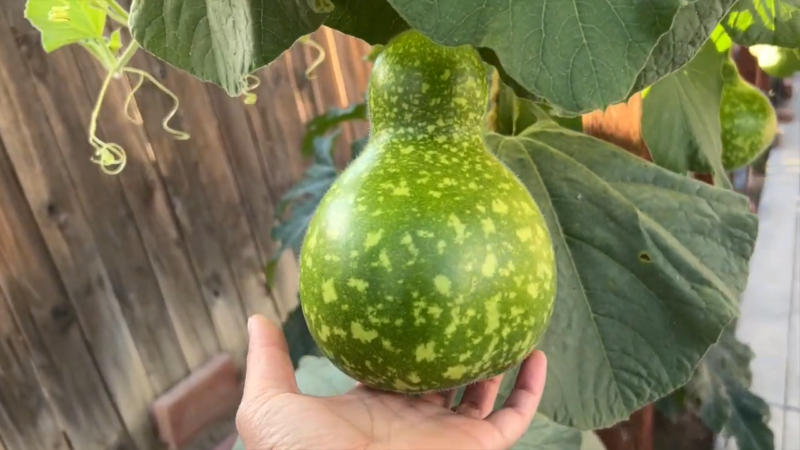
2. Desert Gourd (Citrullus colocynthis)

- Key Characteristics:
- Extensive root system for deep water access
- Sprawling growth pattern with vine-like stems
- Produces small, bitter fruits used in traditional medicine
- Utilized in sand dune stabilization and soil erosion prevention
The only thing that needs to be done is the extraction of a very bitter pulp. The desert gourd is a hardy plant found throughout the Sahara. It has a sprawling growth pattern, with vines that can spread across the ground.
The plant produces small, hard fruits that are used in traditional medicine despite their bitter taste. Desert gourds are known for their ability to survive long periods of drought, relying on their extensive root system to access deep water sources. This plant has various uses beyond traditional medicine. It is often used to stabilize sand dunes and prevent soil erosion. Its resilience and adaptability make it a valuable species in efforts to combat desertification and restore degraded land.
1. Succulent Euphorbia (Euphorbia spp.)
- Key Characteristics:
- Water-storing tissues in thick, fleshy stems
- Toxic sap to deter herbivores
- Unique and varied appearance
- Contributes to soil stabilization and supports other plants
Succulent Euphorbias are distinctive plants that thrive in the harsh conditions of the Sahara Desert.
They are known for their unique appearance, with thick, fleshy stems that store water. These plants can range in size from small, ground-hugging species to larger shrubs.
Euphorbias often have toxic sap, which deters herbivores from feeding on them.
In the desert ecosystem, Euphorbias play a vital role by providing a reliable source of moisture and nutrients for various animals.
Their water-storing tissues make them particularly well-suited to survive long periods without rainfall.
Their presence can help stabilize the soil and support other plant species.
The Bottom Line
These detailed descriptions provide insight into the remarkable adaptations that allow these plants to thrive in the extreme environment of the Sahara Desert.
Each species contributes uniquely to the ecosystem, showcasing the resilience and diversity of desert flora.
Related Posts:
- 6 Unique Plants Found in the Sahara Desert - Rare…
- Top 12 Most Strange Desert Plants - Flora You Won't…
- 10 Ancient Plants Still Used by Nomadic Tribes -…
- What Animal Was Used to Transport Goods Across the…
- What Animals Live In The Sahara Desert? Check Out…
- Why We Must Protect the Sahara Desert Cheetah at all Costs